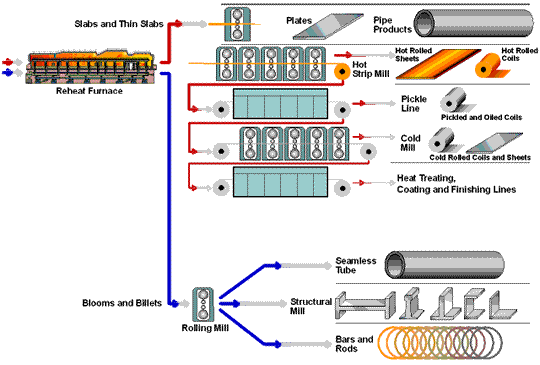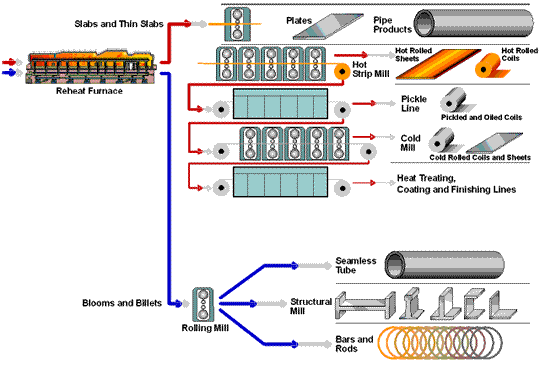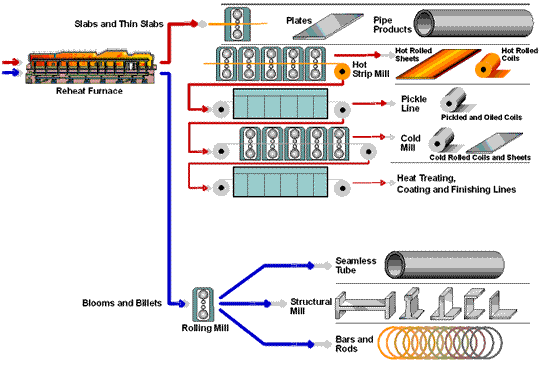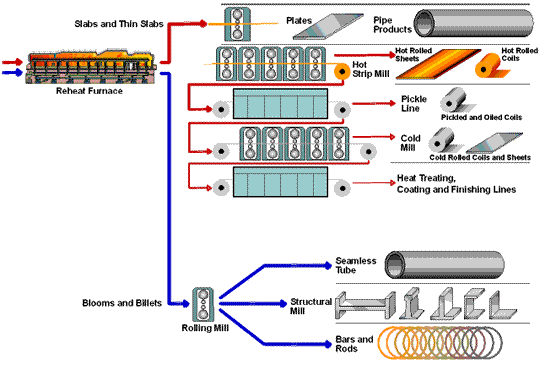
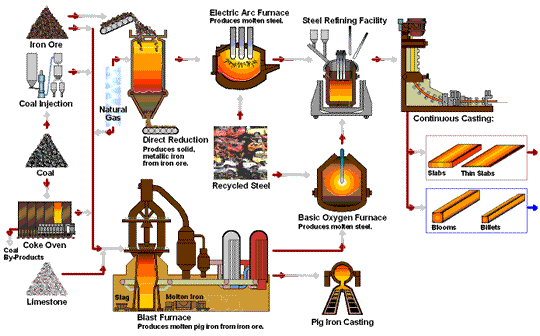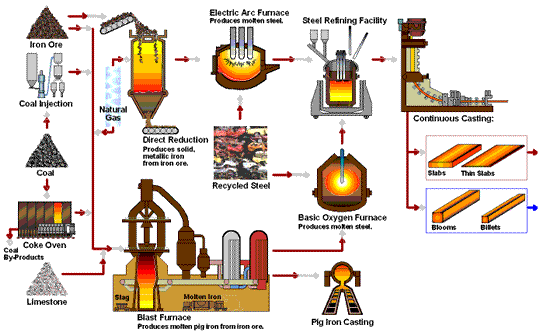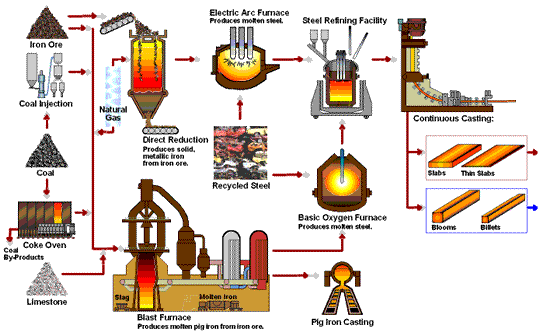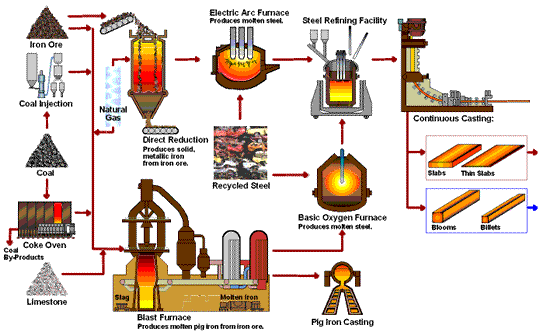
The Material is very important to the Fasteners Quality -- take about 50% proportion of quality issues. All our materials are from reliable sources-- which are mainly from China Steel and from Taiwan only to ensure our quality .
There are Three Systems of Bolt Grades and strength standard
There are three main systems of bolt grades: SAE, ASTM, and ISO.
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) grades bolts according to their strength, ranging from grade 2 to grade 8. Grade 2 is the weakest, and grade 8 is the strongest. We supply the SAE J429 Hex Bolts, SAE J933 SELF TAPPING sCREWS, SAE J81 Tri-lobe Thread Forming Screws , SAE J78 Self Drilling Screws.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) grades bolts according to their chemical composition and physical properties, ranging from grade A to grade F. Grade A is the weakest, and grade F is the strongest, We supply ASTM 307A Hex Bolts, ASTM A325, ASTM A193, ASTM 593 Bolts
- ISO (International Standards Organization) grades bolts according to their material properties, ranging from Class 4.6 to Class 12.9. Class 4.6 is the weakest, and class 12.9 is the strongest per ISO 898-1
We have expeicance handle the production of different materials - included Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Aolly Steel, Brass and Aluminum to meet your usage demand on difficult material requirement. But Carbon steel, takes about 80% of our products.
Carbon Steel Composition
The essential elements of steel are iron and carbon. In general, steels with higher carbon content are hard and brittle, while steels with lower carbon content are ductile and softness.
1) Carbon Steel for FASTENERS -- low carbon Steel and Medium Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is composed of iron and 0.02 - 2.00 percent carbon, with some small amount of impurity elements such as manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), sulfur (S), phosphorus (P), and oxygen (O), etc.
The key factor distinguishing low, medium and high carbon steel is the percentage content of carbon, and according to the different carbon percentage content, it’s divided into the following types:
- Low Carbon Steel: also know as mild steel, the percentage content of carbon is 0.04 (0.05)%-0.25 (or 0.29)%.
with it's softness, very suitable for Cold heasing process, and Heattreated for further usage.
Typical low carbon steels include:
- US ASTM A36,, SAE, AISI 1008, 1012, 1015, 1018, 1020, 1022, 1025, 1029, etc.
- European EN S185, S235, S275, S355, S450, DC01 (St12), etc.
- Medium Carbon Steel: the carbon percentage content is 0.25 (0.30)%-0.60%.
Typical medium carbon steels include:
- US ASTM SAE AISI 1030, 1034, 1035, 1038, 1040, 1042, 1043, 1045, 1050, 1055, etc.
- European EN C35 (1.0501), C40 (1.0511), C45 (1.0503), C55 (1.0535), C60 (1.0601), etc.
- High Carbon Steel: the carbon percentage content is 0.60%-2.0%.
2) Alloy Steel :
Alloy steel is a steel that has had small amounts of one or more alloying elements (other than carbon) such as such as manganese, silicon, nickel, titanium, copper, chromium and aluminum added. This produces specific properties that are not found in regular carbon steel. Alloy steels are workhorses of industry because of their economical cost, wide availability, ease of processing, and good mechanical properties. Alloy steels are generally more responsive to heat and mechanical treatments than carbon steels.
SCM 435 Chemical Component:
|
Material |
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S |
Ni |
Cr |
Mo |
|
SCM435 |
0.33 |
0.15 |
0.60 |
0.030 Max |
0.030 Max |
0.25 Max |
0.90 |
0.15 |
AISI 4140:Chemical Component:
|
C |
Cr |
Mn |
Si |
Mo |
S |
P |
Fe |
|
0.38-.43% |
0.80-1.10% |
0.75-1.0% |
0.15-0.30% |
0.15-0.25% |
0.040% max |
0.035% max |
Balance |
10B21 Chemical Component:
|
10B21 |
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S |
V |
B |
|
0.18-0.23 |
Under0.10 |
0.70-1.0 |
under0.030 |
under0.035 |
- |
above 0.0005 |
10B33 Chemical Component:
|
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S |
V |
B |
|
|
10B33 |
0.32-0.36 |
0.15-0.35 |
0.70-1.0 |
under0.030 |
under0.035 |
- |
above 0.0005 |
3) Stainless Steel :
Stainless steel is an alloy of Iron with a minimum of 10.5% Chromium. Chromium produces a thin layer of oxide on the surface of the steel known as the 'passive layer'. This prevents any further corrosion of the surface. Increasing the amount of Chromium gives an increased resistance to corrosion.
300 series
This series is used to name austenitic stainless steels with carbon, nickel, and molybdenum as alloying elements. The addition of molybdenum improves corrosion resistance in acidic environments while nickel improves ductility.
AISI 304 and 316 are the most common grades in this series. AISI 304 is also commonly known as 18/8 steel as it contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel.
400 series
Ferritic and martensitic alloys form this series of stainless steel. These grades are available for heat treating. Providing a good combination of strength and high wear resistance. The corrosion-resistance properties are lower than 300 series, though.
Stainless Steel Mechanical Properties
4 ) C26000 Cartridge Brass "70/30" (CDA 260)
Chemical Properties
(%max., unless shown as range or min.)
| ELEMENT | CU (1) | PB | ZN | FE |
| Min % | 68.5 | |||
| Max % | 71.5 | 0.07 | Rem | 0.05 |
Note: Cu + Sum of Named Elements, 99.7% min.